Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition characterised by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. There are two main types: ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD)1,2.


Ulcerative colitis (UC) is an idiopathic inflammatory disorder primarily affecting the colon and rectum. It is characterised by chronic inflammation and ulceration of the mucosal lining of the colon. The exact cause of UC is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune factors1,2,3. UC is also associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer4.


Crohn's disease (CD) is characterised by inflammation and damage to the lining of the digestive tract, which can occur anywhere from the mouth to the anus. CD is not limited to specific lesion sites and can involve any part of the digestive tract, including the small intestine, large intestine, and even the perianal area. The exact cause of CD is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune factors. The harms associated with CD include complications such as strictures, fistulas, abscesses, and malnutrition1,2,5.



.png)

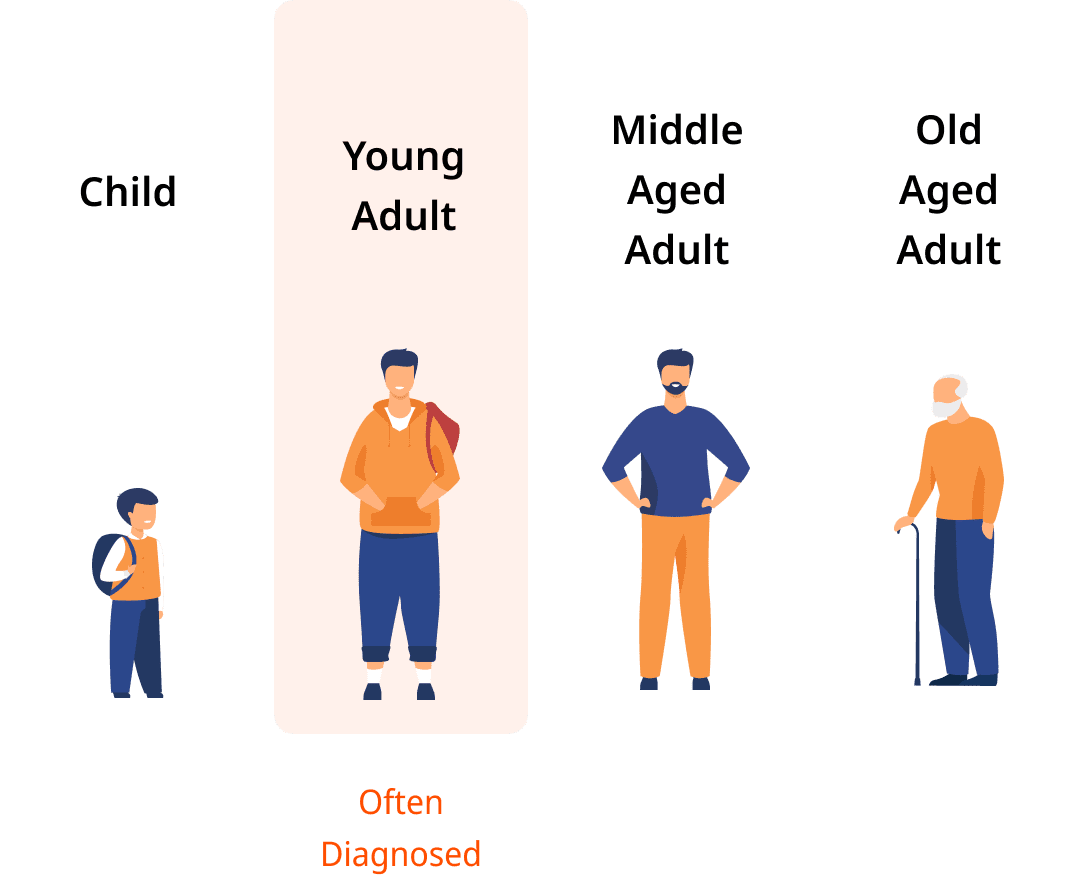


The severity of IBD varies from mild to severe, and is classified according to symptom severitys.
